Interoperability is the ability of two or more systems or components to exchange information and to use the information that has been exchanged. Geraci et al. (1991)
In healthcare, there is a need for systems that allows seamless exchange of information across these various sources without any loss of meaning. This ability to communicate and exchange data is termed interoperability.
Interoperability is essential in healthcare because patient data originates from various sources, including clinical laboratories, radiology, pharmacies, and clinician notes, all of which must be accessible when needed for care. Also, patients often switch caregivers due to factors like proximity, emergencies, or perceived quality of care, leading to isolated data silos that hinder a comprehensive view of the patient. Interoperability bridges these silos, offering a comprehensive patient view and improving care delivery.
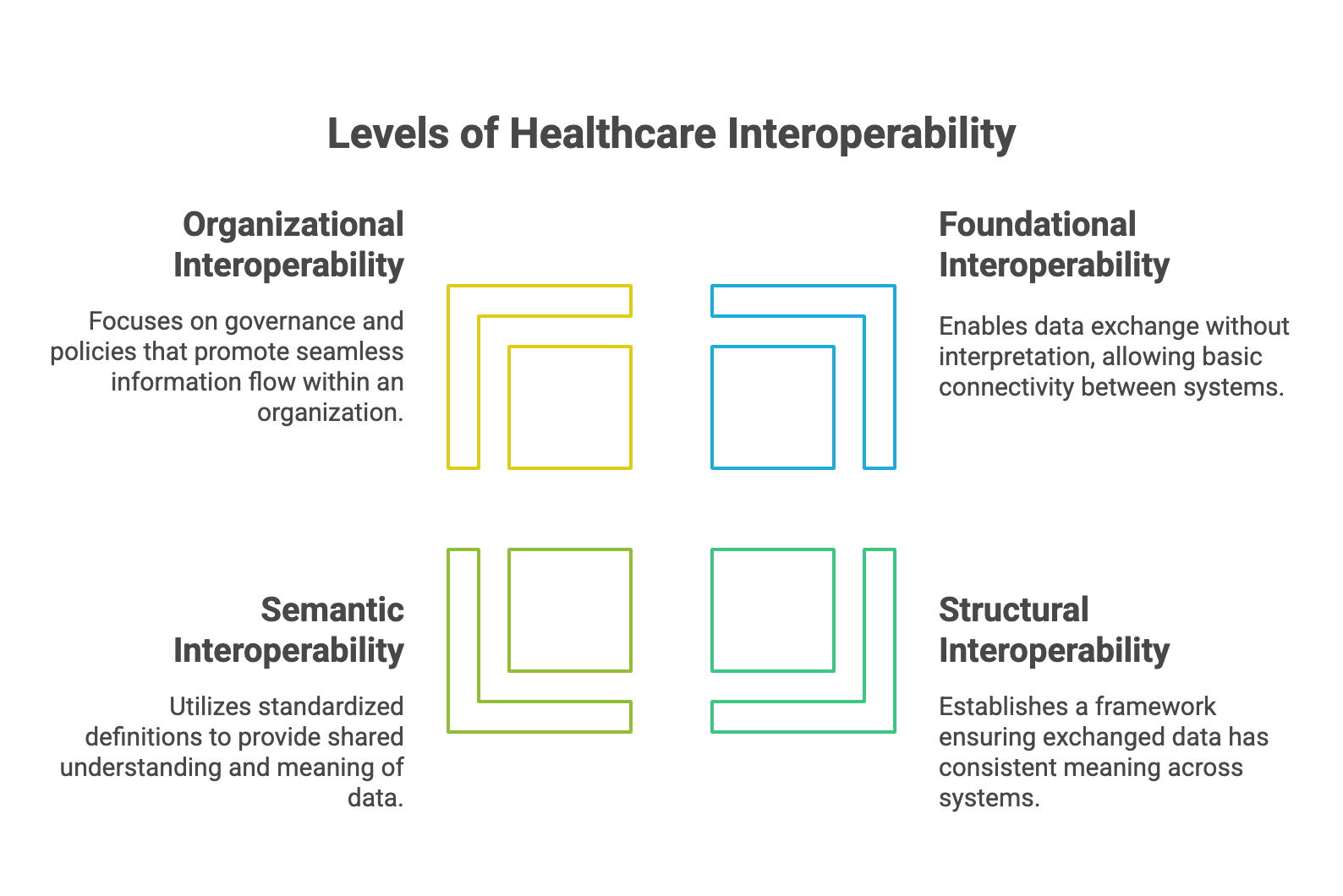
Four levels of interoperability have been identified by Healthcare Information and Management Systems Society (HIMSS) namely foundation, structural and semantic interoperability.
- Foundational interoperability allows for data to be sent between systems, but the data cannot be interpreted.
- In Structural interoperability, a structure is made that ensures that exchanged data convey the same meaning between the sending and receiving systems.
- Semantic interoperability occurs when there is a codification of data elements using standardized definitions from publicly available value sets and coding vocabularies, providing shared understanding and meaning to the user.
- Organizational interoperability involves creating an enterprise wide policy and governance that encourages the seamless flow of information between systems ans users.
Over the years, several healthcare standards have been developed and maintained by Standard Developing Organizations including
- HL7
- is primarily a structural interoperability SDO, focused on the format and syntax of data exchange. They develop and maintain frameworks for sharing and integrating electronic health data. Such standards include HL7 version 2 & 3, Clinical Document Architecture (CDA) and Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR).
- SNOMED
- develops SNOMED CT, a standardized terminology for clinical concepts (e.g., diseases, symptoms) used in EHRs to ensure consistent recording and sharing of data.
- WHO
- maintains ICD Codes which classifies diseases and health conditions and is used primarily for billing and reporting
- LOINC
- maintains LOINC codes used in standardizing laboratory tests and clinical measurements.
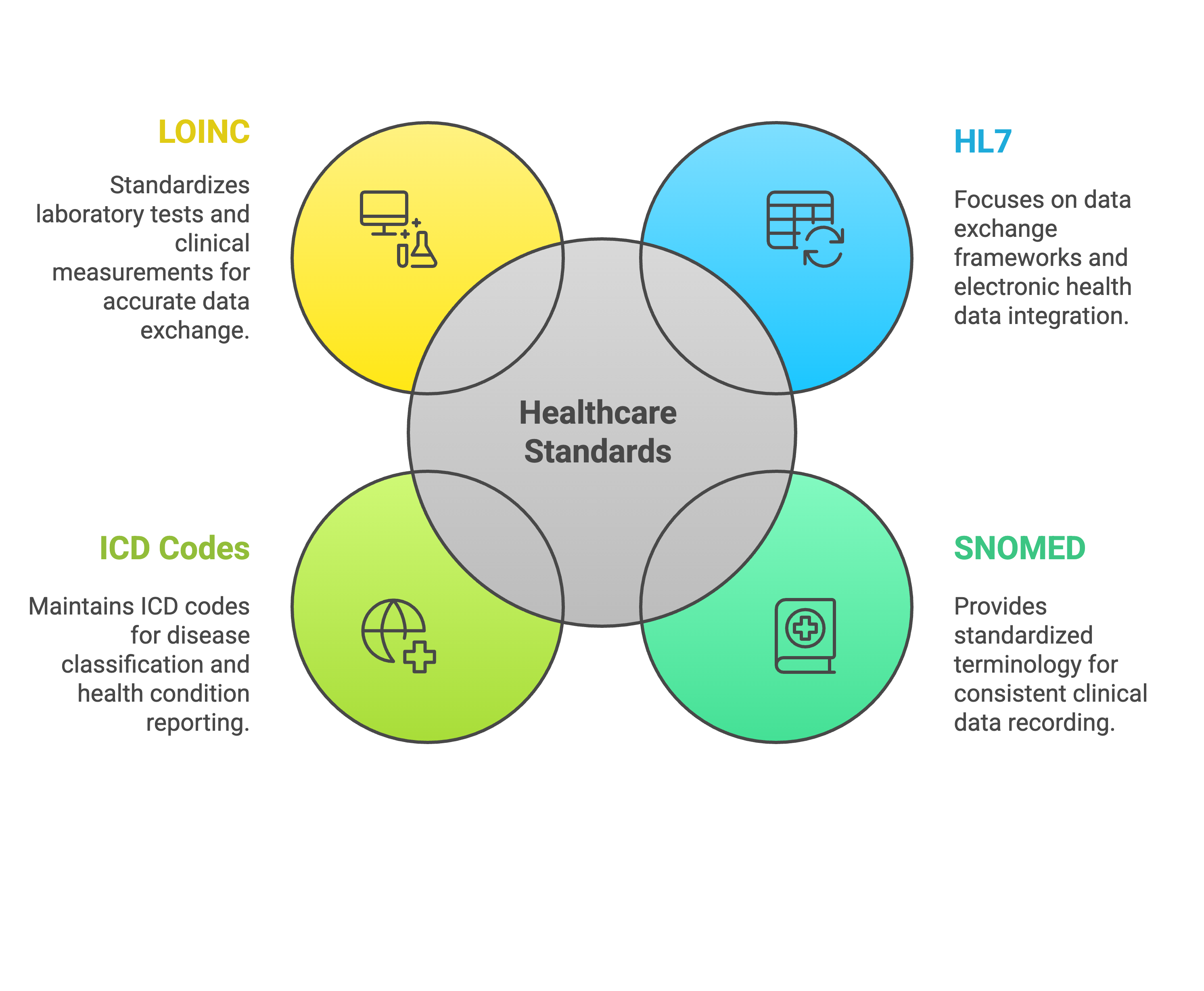
These standards ensure accurate, meaningful data exchange in healthcare, enabling better care coordination and outcomes.